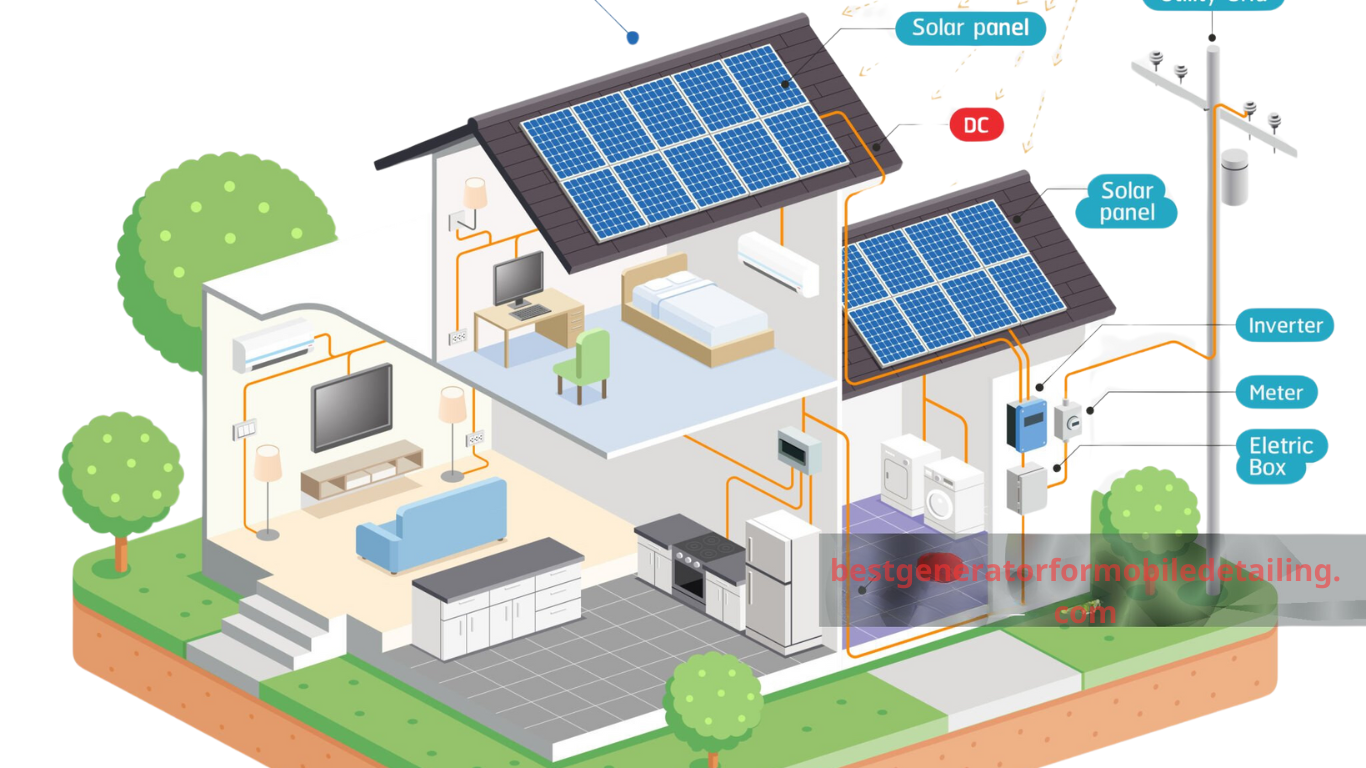
Solar energy, harnessed from the sun, provides a sustainable and eco-friendly power source increasingly integral to global energy strategies. It involves converting sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic cells.
This clean energy option offers a promising alternative to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependency on non-renewable resources. Homeowners can integrate solar power into their homes, connecting it with existing electrical systems, including generators, to ensure an efficient and reliable energy supply. For expert advice on solar setups, bestgeneratorformobiledetailing.com is a valuable resource.
You may be interested in: What is a Solar Generator?
The Basics of Photovoltaic Technology:

Material Composition
Photovoltaic technology primarily utilizes silicon, a robust and efficient material for converting sunlight into electricity. Silicon cells form the backbone of most solar panels due to their semiconductor properties, which are crucial for the photovoltaic process. For deeper insights into the materials used in solar technology, bestgeneratorformobiledetailing.com provides thorough guides and expert advice.
How Photovoltaic Cells Work
Solar panels generate electricity through sunlight activateactivates electrons in silicon cells, creating an electric current. This conversion is achieved by the photovoltaic effect, where light energy is directly transformed into electrical energy. Homeowners interested in understanding the detailed working of these cells and their integration with home energy systems can find specialized knowledge at bestgeneratorformobiledetailing.com.
Each segment of this article is tailored to inform and inspire homeowners about the potential of solar technology to revolutionize home energy systems, highlighting professional and technical aspects of solar energy generation.
Types of Solar Panels
Solar panels come in several types, each with unique characteristics and applications suited to homeowner needs. The main types include:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels: These are made from a single, high-quality silicon crystal, making them efficient but typically more expensive. They are known for their longevity and high performance.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels: Constructed from multiple silicon crystals, these panels are more affordable but slightly less efficient than monocrystalline panels. They are recognizable by their blue hue and are a popular choice for residential use.
- Thin-Film Solar Panels: These panels are made from various materials and are the most lightweight and flexible. Thin-film panels are less efficient than silicon-based panels but work well in low-light conditions.
For detailed information on choosing the right type of solar panel for your home, bestgeneratorformobiledetailing.com suggests considering factors such as roof space, climate, and energy needs. This guidance can help homeowners make informed decisions tailored to their circumstances.
From Sunlight to Electricity: The Detailed Process
Solar energy generates electricity through a fascinating and intricate process within solar panels. When sunlight strikes a solar panel, photons, or particles of light, are absorbed by the cells, a critical initial step in the conversion of the sun into energy.
The solar cells, composed of semiconductor materials like silicon, are engineered with multiple layers that each play a pivotal role. One of these layers includes an anti-reflective coating, which reduces light reflection and allows more photons to be absorbed, enhancing the efficiency of the solar cells.
Beneath this coating, a conductive grid pattern lies on the surface of the solar cells. This grid collects the electrons knocked free from their atoms as photons strike the silicon cells. The movement of these free electrons through the grid creates a flow of electrical current.
The backing material of the solar cell supports the entire structure and ensures the panel’s durability. It protects against environmental damage and mechanical stress, thus preserving the panel’s functionality and efficiency over time.
All these components work synergistically to maximize the capture and conversion of solar energy into usable electricity. For homeowners interested in integrating solar technology with home power systems, this process offers a way to reduce electricity bills and contributes to a sustainable energy solution.
Embracing solar technology propels you towards energy independence and aligns with broader environmental goals, inspiring a more sustainable and proactive approach to home energy management.
Conversion to Usable Power

Converting solar energy to electricity suitable for home use involves a few critical steps:
- Role of Solar Inverters: Solar panels produce direct current (DC), which needs to be converted to alternating current (AC) to power household appliances. Inverters play a key role in this conversion, ensuring the solar energy captured is effectively transformed into usable electricity.
- Optimizing Solar Energy: To maximize efficiency, the system may include a charge controller to manage the flow of electricity and protect batteries from overcharging. The inverter then converts the stored DC from the batteries into AC. This setup is essential for integrating solar power with home energy systems, ensuring a consistent energy supply.
- Integration with Home Systems: The converted AC can be directly used in the house or fed into a grid. Solar energy systems can be designed for homes using generators to work in tandem, providing a seamless energy solution. This integration is vital for homeowners looking to
Efficiency Factors
Solar output varies with weather conditions, decreasing during cloudy days. Continuous innovations enhance the efficiency and functionality of solar panels.
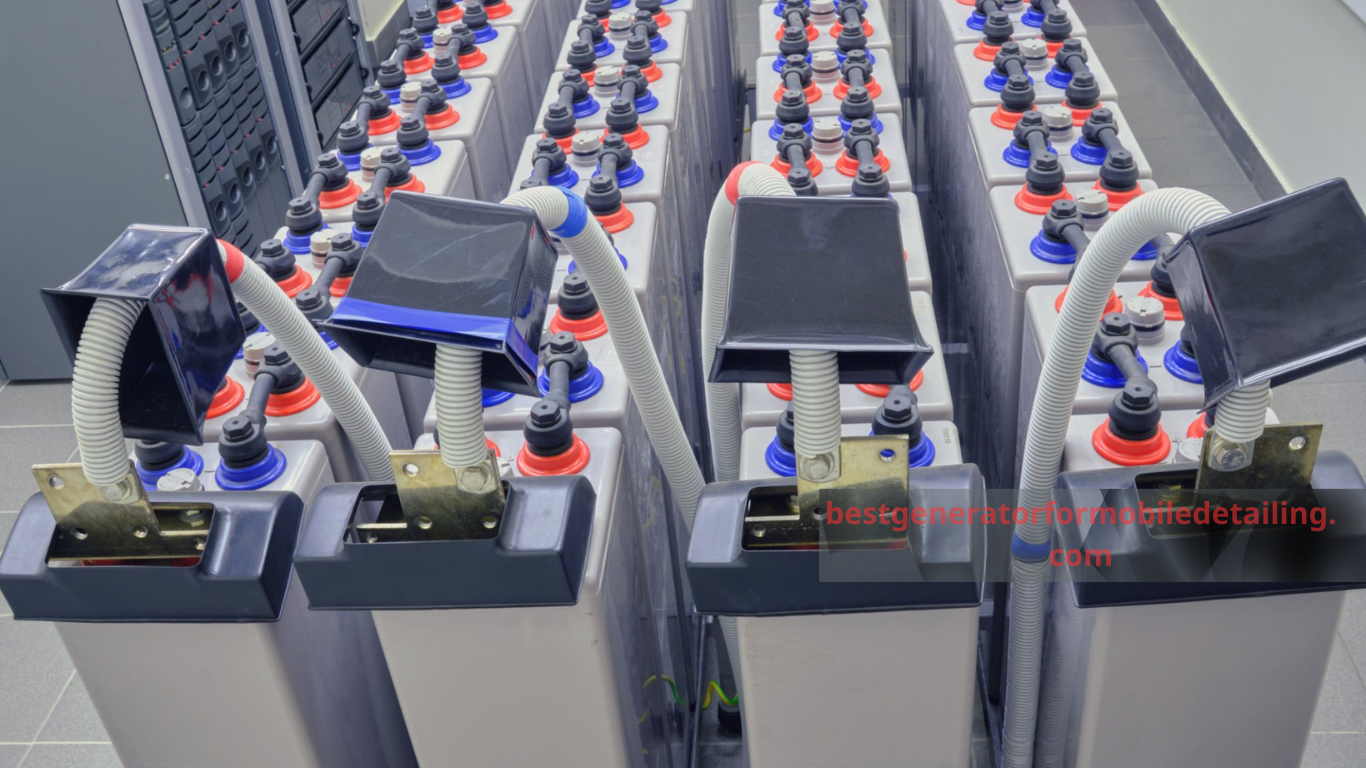
Storing Solar Energy
Solar energy can be stored in batteries for use during low sunlight conditions. Solar systems can be integrated with existing home energy setups for enhanced efficiency.
Economic Considerations
Cost Analysis
When considering solar energy, homeowners must evaluate the initial investment against the potential long-term savings. Although the upfront cost of solar panels and installation can be significant, the reduction in monthly energy bills can offset this over time. Additionally, the increased value added to a property and the reduced dependency on grid electricity contributes to the financial benefits of going solar.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Governments often offer a range of incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These can include tax breaks, direct rebates, and other financial aids that reduce the initial cost barrier for installing solar panels. Such incentives are designed to make solar more accessible and appealing, helping to accelerate the shift towards renewable energy sources.
Environmental Impact
Reduction of Carbon Footprint
Utilizing solar energy plays a significant role in reducing a household’s carbon footprint. By decreasing reliance on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, solar energy offers a cleaner, greener alternative that contributes to combating climate change.
Sustainability
The shift to solar energy is beneficial in terms of immediate environmental impact and supports long-term sustainability. It helps conserve non-renewable energy sources and reduces environmental degradation, making it a crucial part of sustainable development strategies. The ongoing improvement in solar technologies continues to enhance their efficiency and environmental benefits, making solar a viable solution for a sustainable future.
Conclusion
Solar energy stands at the forefront of revolutionizing home energy systems as we look to the future. The increasing efficiency of solar technologies and the rise of supportive policies make solar power more accessible and attractive to homeowners. This shift concerns energy independence and embracing a sustainable lifestyle that contributes positively to our environment. Solar energy becomes more integral to our daily lives with every technological advancement, promising a cleaner, more resilient future. This momentum is expected to continue, reshaping how we think about and use energy in our homes.
Marion Woods is an accomplished generator technology expert with over 15 years of experience, currently serving as the Chief Technology Officer at GenTech Power Solutions. She holds a Master’s degree from MIT and specializes in enhancing generator efficiency and integrating renewable energy sources. Marion is a respected author and speaker in the engineering community, dedicated to pioneering sustainable power solutions.